1.通过yum 方式 安装quota
#yum install quota
2.VirtualBox创建硬盘
如果你的Linux环境建立在VirtualBox下:
(1)关闭虚拟机镜像
点击setting 配置虚拟机所使用的硬件
(2)配置新硬盘
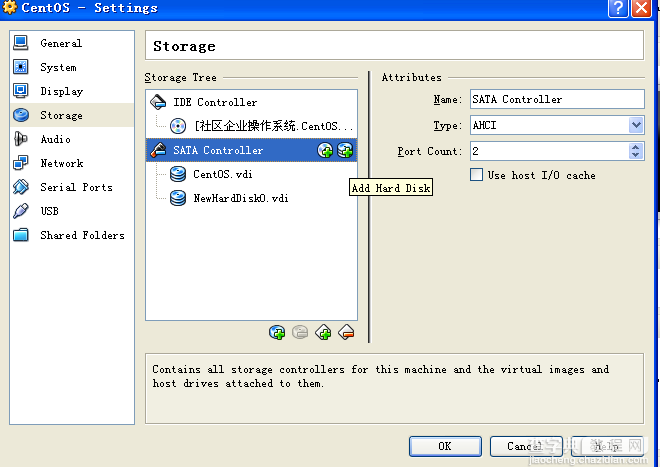
选择Create new disk
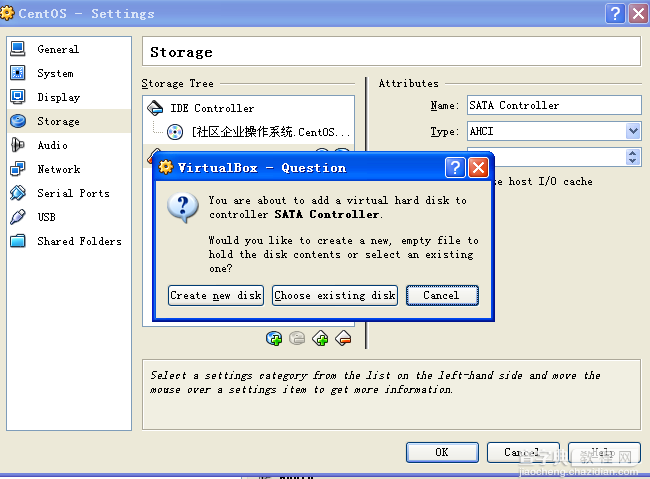
选择VHD (virtual hard disk)
输入硬盘镜像名字
(3)格式化硬盘
进入linux,使用命令创建硬盘进行格式化
#mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb
(4)为硬盘空间寻找目录
#mount /dev/sdb /home
如果有需要长期挂着,请自行百度如何修改/etc/fstab,本人修改多次,让系统多次崩溃,最终放弃,选择在 vi /etc/rc.local 里面,业余的加入 mount /dev/sdb /home 这条命令。
3.格式化新创建的硬盘
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb
mke2fs 1.41.12 (12-Apr-2016)
/dev/sdb is entire device, not just one partition!
Proceed anyway? (y,n) y
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
524288 inodes, 2097152 blocks
104857 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2147483648
64 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 24 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
挂在硬盘到/home目录
[root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sdb /home/
[root@localhost ~]# mount -o remount,usrquota,grpquota /home
[root@localhost ~]# mount
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root on / type ext4 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620)
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw,rootcontext="system_u:object_r:tmpfs_t:s0")
/dev/sda1 on /boot type ext4 (rw)
none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
/dev/sdb on /home type ext4 (rw,usrquota,grpquota)
为系统设置启动后自动挂载硬盘
[root@localhost ~]#vi /etc/rc.local
添加
mount /dev/sdb /home
mount -o remount,usrquota,grpquota /home
备注:本人并没有采取修改/etc/fstab 的方法,因为该方法容易因为输入的字符或格式不对导致系统崩溃,所以采取了修改用户启动文件的方法
4.配置quota
[root@localhost ~]#quotacheck -avug 对整个系统含有 usrquota, grpquota 参数的文件系统进行 quotacheck 扫描
quotacheck: Your kernel probably supports journaled quota but you are not using it. Consider switching to journaled quota to avoid running quotacheck after an unclean shutdown.
quotacheck: Scanning /dev/sdb [/home] done
quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Checked 2 directories and 0 files
quotacheck: Cannot create new quotafile /home/aquota.user.new: Permission denied
quotacheck: Cannot initialize IO on new quotafile: Permission denied
quotacheck: Cannot create new quotafile /home/aquota.group.new: Permission denied
quotacheck: Cannot initialize IO on new quotafile: Permission denied
出现报错,报错原因是因为没有关闭selinux
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# quotacheck -avug
quotacheck: Your kernel probably supports journaled quota but you are not using it. Consider switching to journaled quota to avoid running quotacheck after an unclean shutdown.
quotacheck: Scanning /dev/sdb [/home] done
quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file: No such file or directory
quotacheck: Checked 2 directories and 0 files
quotacheck: Old file not found.
quotacheck: Old file not found.
成功生成
[root@localhost ~]#quotaon -auvg 启动quota
5.为用户添加硬盘空间限制
创建账户
[root@localhost ~]# useradd quotauser1
[root@localhost ~]# passwd quotauser1
[root@localhost ~]# edquota -u quotauser1
Disk quotas for user quotauser1 (uid 500):
Filesystem blocks soft hard inodes soft hard
/dev/sdb 16 500000 600000 4 0 0
限制用户quotauser1的使用空间为500M,最大限制是600M
参数意义参考
soft :这是最低限制容量的意思,使用者在宽限期间之内,他的容量可以超过 soft ,但必需要宽限时间之内将磁盘容量降低到 soft 的容量限制之下!
hard :这是『绝对不能超过』的容量!跟 soft 相比的意思为何呢?通常 hard limit 会比 soft limit 为高,例如网络磁盘空间为 30 MB ,那么 hard limit 就设定为 30MB ,但是为了让使用者有一定的警戒心,所以当使用空间超过 25 MB 时,例如使用者使用了 27 MB 的空间时,那么系统就会警告使用者,让使用者可以在『宽限时间内』将他的档案量降低至 25 MB ( 亦即是 soft limit )之内!也就是说, soft 到 hard 之间的容量其实就是宽限的容量啦!可以达到针对使用者的『警示』作用!
宽限时间:那么宽限时间就可以很清楚的知道含意是什么了!也就是当您的使用者使用的空间超过了 soft limit ,却还没有到达 hard limit 时,那么在这个『宽限时间』之内,就必需要请使用者将使用的磁盘容量降低到 soft limit 之下!而当使用者将磁盘容量使用情况超过 soft limit 时,『宽限时间』就会自动被启动,而在使用者将容量降低到 soft limit 之下,那么宽限时间就会自动的取消啰!
6.测试
登陆quotauser1
创建超过600M的文件
[quotauser1@localhost ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=bigfile bs=1M count=700
sdb: warning, user block quota exceeded.
sdb: write failed, user block limit reached.
dd: writing `bigfile': Disk quota exceeded
586+0 records in
585+0 records out
614379520 bytes (614 MB) copied, 2.75934 s, 223 MB/s
[quotauser1@localhost ~]$ ls
bigfile
[quotauser1@localhost ~]$ ls -l
total 599984
-rw-rw-r--. 1 quotauser1 quotauser1 614379520 Sep 28 03:28 bigfile
可以发现文件的大小被限制了


