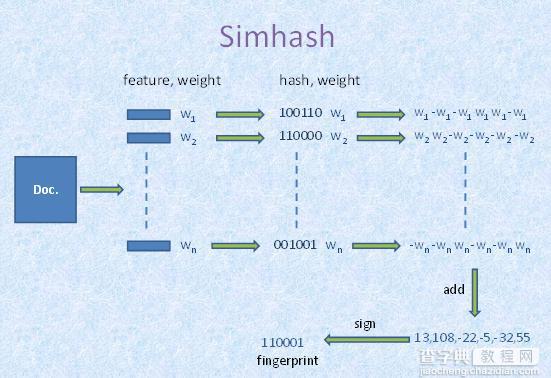
Simhash的算法简单的来说就是,从海量文本中快速搜索和已知simhash相差小于k位的simhash集合,这里每个文本都可以用一个simhash值来代表,一个simhash有64bit,相似的文本,64bit也相似,论文中k的经验值为3。该方法的缺点如优点一样明显,主要有两点,对于短文本,k值很敏感;另一个是由于算法是以空间换时间,系统内存吃不消。
复制代码 代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding=utf-8
class simhash:
#构造函数
def __init__(self, tokens='', hashbits=128):
self.hashbits = hashbits
self.hash = self.simhash(tokens);
#toString函数
def __str__(self):
return str(self.hash)
#生成simhash值
def simhash(self, tokens):
v = [0] * self.hashbits
for t in [self._string_hash(x) for x in tokens]: #t为token的普通hash值
for i in range(self.hashbits):
bitmask = 1 << i
if t & bitmask :
v[i] += 1 #查看当前bit位是否为1,是的话将该位+1
else:
v[i] -= 1 #否则的话,该位-1
fingerprint = 0
for i in range(self.hashbits):
if v[i] >= 0:
fingerprint += 1 << i
return fingerprint #整个文档的fingerprint为最终各个位>=0的和
#求海明距离
def hamming_distance(self, other):
x = (self.hash ^ other.hash) & ((1 << self.hashbits) - 1)
tot = 0;
while x :
tot += 1
x &= x - 1
return tot
#求相似度
def similarity (self, other):
a = float(self.hash)
b = float(other.hash)
if a > b : return b / a
else: return a / b
#针对source生成hash值 (一个可变长度版本的Python的内置散列)
def _string_hash(self, source):
if source == "":
return 0
else:
x = ord(source[0]) << 7
m = 1000003
mask = 2 ** self.hashbits - 1
for c in source:
x = ((x * m) ^ ord(c)) & mask
x ^= len(source)
if x == -1:
x = -2
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = 'This is a test string for testing'
hash1 = simhash(s.split())
s = 'This is a test string for testing also'
hash2 = simhash(s.split())
s = 'nai nai ge xiong cao'
hash3 = simhash(s.split())
print(hash1.hamming_distance(hash2) , " " , hash1.similarity(hash2))
print(hash1.hamming_distance(hash3) , " " , hash1.similarity(hash3))


