先看效果图
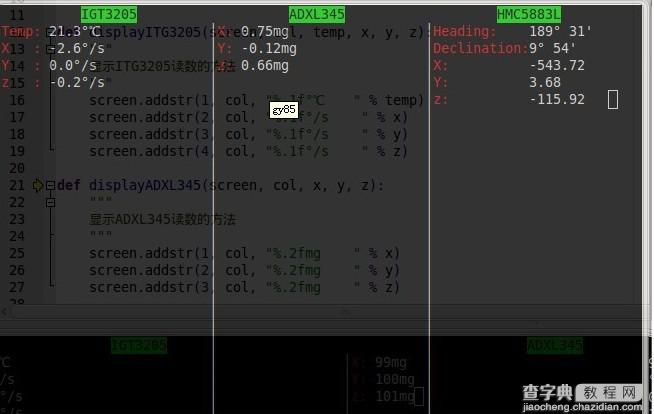 |
GY-85.py:
复制代码 代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import curses
from time import *
from i2clibraries import i2c_itg3205, i2c_adxl345, i2c_hmc5883l
#==========================================================
# GY-85传感器监控
#==========================================================
def displayITG3205(screen, col, temp, x, y, z):
"""
显示ITG3205读数的方法
"""
screen.addstr(1, col, "%.1f°℃ " % temp)
screen.addstr(2, col, "%.1f°/s " % x)
screen.addstr(3, col, "%.1f°/s " % y)
screen.addstr(4, col, "%.1f°/s " % z)
def displayADXL345(screen, col, x, y, z):
"""
显示ADXL345读数的方法
"""
screen.addstr(1, col, "%.2fmg " % x)
screen.addstr(2, col, "%.2fmg " % y)
screen.addstr(3, col, "%.2fmg " % z)
def displayHMC5883L(screen, col, heading, declination, x, y, z):
"""
显示MC5883L读数的方法
"""
screen.addstr(1, col, heading + " ")
screen.addstr(2, col, declination + " ")
screen.addstr(3, col, "%.2f " % x)
screen.addstr(4, col, "%.2f " % y)
screen.addstr(5, col, "%.2f " % z)
try:
myscreen = curses.initscr() #初始化curses
myscreen.border(0)
(screen_h, screen_w) = myscreen.getmaxyx() #获得屏幕高宽
curses.start_color() #设置颜色
curses.init_pair(1, curses.COLOR_BLACK, curses.COLOR_GREEN) #绿底黑字
curses.init_pair(2, curses.COLOR_RED, curses.COLOR_BLACK) #白底蓝字
curses.init_pair(3, curses.COLOR_MAGENTA,curses.COLOR_BLACK) #黑底什么字
myscreen.clear() #清除画布
# 计算每块的坐标, 屏幕分3列, 每列显示一个传感器
col1 = screen_w / 3 * 0
col2 = screen_w / 3 * 1
col3 = screen_w / 3 * 2
# 屏幕横向分三块,每块中间写上标题
myscreen.addstr(0, int(col1 + screen_w / 3 / 2 - 3), "IGT3205", curses.color_pair(1))
myscreen.addstr(0, int(col2 + screen_w / 3 / 2 - 4), "ADXL345", curses.color_pair(1))
myscreen.addstr(0, int(col3 + screen_w / 3 / 2 - 4), "HMC5883L", curses.color_pair(1))
#画分割线,把屏幕分为3列
for col in range(1, screen_h):
myscreen.addstr(col, int(col2), "│")
myscreen.addstr(col, int(col3), "│")
# 事先打印IGT3205的各项值的名称
myscreen.addstr(1, int(col1), "Temp:", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(2, int(col1), "X :", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(3, int(col1), "Y :", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(4, int(col1), "z :", curses.color_pair(2))
# 事先打印ADXL345的各项值的名称
myscreen.addstr(1, int(col2) + 1, "X:", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(2, int(col2) + 1, "Y:", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(3, int(col2) + 1, "z:", curses.color_pair(2))
# 事先打印HMC5883L的各项值的名称
myscreen.addstr(1, int(col3) + 1, "Heading: ", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(2, int(col3) + 1, "Declination:", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(3, int(col3) + 1, "X: ", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(4, int(col3) + 1, "Y: ", curses.color_pair(2))
myscreen.addstr(5, int(col3) + 1, "z: ", curses.color_pair(2))
# 初始化传感器
itg3205 = i2c_itg3205.i2c_itg3205(0)
adxl345 = i2c_adxl345.i2c_adxl345(0)
hmc5883l = i2c_hmc5883l.i2c_hmc5883l(0)
hmc5883l.setContinuousMode() #设置为持续更新模式
hmc5883l.setDeclination(9,54) #设置真北磁偏角补偿
while True:
#读取itg3205数据
(itgready, dataready) = itg3205.getInterruptStatus()
if dataready:
temp = itg3205.getDieTemperature()
(x, y, z) = itg3205.getDegPerSecAxes()
displayITG3205(myscreen, 6, temp, x, y, z) #刷新画布
#读取adxl345数据
(x, y, z) = adxl345.getAxes()
displayADXL345(myscreen, int(col2) + 4, x, y, z) #刷新画布
#读取hmc5883l数据
(x, y, z) = hmc5883l.getAxes()
heading = hmc5883l.getHeadingString() #获取指向角度
declination = hmc5883l.getDeclinationString() #获取磁偏角补偿信息
displayHMC5883L(myscreen, int(col3) + 13, heading, declination, x, y, z) #刷新画布
myscreen.refresh() #应用画布
sleep(0.1) #暂停0.1秒
myscreen.getch()
finally:
curses.endwin()


