1.委托
总的来说,委托是一个类,它定义了方法的类型,使得可以将方法当作另一个方法的参数来进行传递,这种将方法动态地赋给参数的做法,可以避免在程序中大量使用If-Else(Switch)语句,同时使得程序具有更好的可扩展性。所以,引入委托后,编程人员可以把方法的引用封装在委托对象中,然后把委托对象传递给需要引用方法。调用委托和调用方法的方式是一模一样的,代码如下:
a.代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WForms
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
//定义委托
private delegate void WriteTextBox(char ch);
//声明委托
private WriteTextBox writeTextBox;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (checkBox1.Checked == true)
{
textBox1.Clear();
textBox1.Refresh();
// 实例化委托- 方法WriteTextBox1
writeTextBox = new WriteTextBox(WriteTextBox1);
// 委托作为参数,在方法WriteText通过委托运行WriteTextBox1方法
WriteText(writeTextBox);
textBox3.Focus();
textBox3.SelectAll();
}
if (checkBox2.Checked == true)
{
textBox2.Clear();
textBox2.Refresh();
// 实例化委托 - 方法WriteTextBox2作为参数
writeTextBox = new WriteTextBox(WriteTextBox2);
// 委托作为参数,在方法WriteText通过委托运行WriteTextBox2方法
WriteText(writeTextBox);
textBox3.Focus();
textBox3.SelectAll();
}
}
/**
*我们通过WriteText方法来向文本区写入内容,
*它所执行的只是抽象的”写文本“操作,至于究竟向哪个文本框写入文字,
*对于编写WriteText方法的程序来说是不知道,委托writeTextBox就像一个接口一样,
*屏蔽了操作对象的差别(方法到底是想向文本区1写入文本还是像文本区2写入文本,
*现在我方法里面不需要去关心,
*我只需要集中在实现”书写文本”这个操作,而不必纠结操作对象的选择)。
*/
private void WriteText(WriteTextBox writetextbox)
{
string data = textBox3.Text;
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
{
// 使用委托 - 通过委托的不同运行不同的方法
writetextbox(data[i]);
//间歇延时
DateTime now = DateTime.Now;
while (now.AddSeconds(1) > DateTime.Now) { }
}
}
//向文本区1添加字符
private void WriteTextBox1(char ch)
{
textBox1.AppendText(ch.ToString());
}
//向文本区2添加字符
private void WriteTextBox2(char ch)
{
textBox2.AppendText(ch.ToString());
}
}
}
Form1.cs
b.效果图:

2.委托链
其实委托链就是一个委托,只是包含了多个委托而已。看完下面代码,应该可以很明白。
a.代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
// 声明一个委托类型,它的实例引用一个方法,该方法返回一个string类型
public delegate string DelegateTest();
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 用静态方法来实例化委托
DelegateTest dtstatic = new DelegateTest(Program.method1);
// 用实例方法来实例化委托
DelegateTest dtinstance = new DelegateTest(new Program().method2);
DelegateTest dtinstance2 = new DelegateTest(new Program().method3);
// 定义一个委托链对象,一开始初始化为null,就是不代表任何方法(我就是我,我不代表任何人)
DelegateTest delegatechain = null;
delegatechain += dtstatic;
delegatechain += dtinstance;
delegatechain += dtinstance2;
// Environment.NewLine - 换行符
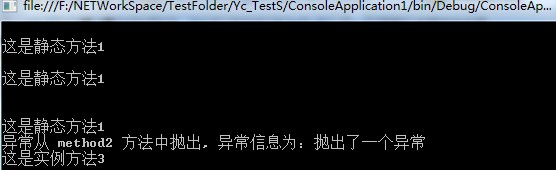
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine + dtstatic() + Environment.NewLine);// 隐式调用委托
Console.WriteLine(dtstatic.Invoke() + Environment.NewLine);// 显式调用委托
Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine + Test(delegatechain));//输出字符串
Console.Read();
}
private static string method1()
{
return "这是静态方法1";
}
private string method2()
{
throw new Exception("抛出了一个异常");
}
private string method3()
{
return "这是实例方法3";
}
// 测试调用委托的方法
private static string Test(DelegateTest chain)
{
if (chain == null)
{
return null;
}
// 用这个变量来保存输出的字符串
StringBuilder returnstring = new StringBuilder();
// GetInvocationList方法返回一个由Delegate引用构成的数组,
//其中每一个数组都指向链中的一个委托对象。
Delegate[] delegatearray = chain.GetInvocationList();
// 遍历数组中的每个委托
foreach (DelegateTest t in delegatearray)
{
try
{
//调用委托获得返回值
returnstring.Append(t() + Environment.NewLine);
}
catch (Exception e)//异常
{
returnstring.AppendFormat("异常从 {0} 方法中抛出, 异常信息为:{1}{2}", t.Method.Name, e.Message, Environment.NewLine);
}
}
// 把结果返回给调用者
return returnstring.ToString();
}
}
}
Program.cs
b.效果图: