测试1
deco运行,但myfunc并没有运行
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(func):
print 'before func'
return func
def myfunc():
print 'myfunc() called'
myfunc = deco(myfunc)
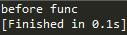
测试2
需要的deco中调用myfunc,这样才可以执行
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(func):
print 'before func'
func()
print 'after func'
return func
def myfunc():
print 'myfunc() called'
myfunc = deco(myfunc)
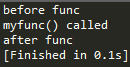
测试3
@函数名 但是它执行了两次
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(func):
print 'before func'
func()
print 'after func'
return func
@deco
def myfunc():
print 'myfunc() called'
myfunc()
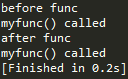
测试4
这样装饰才行
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(func):
def _deco():
print 'before func'
func()
print 'after func'
return _deco
@deco
def myfunc():
print 'myfunc() called'
myfunc()
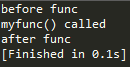
测试5
@带参数,使用嵌套的方法
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(arg):
def _deco(func):
print arg
def __deco():
print 'before func'
func()
print 'after func'
return __deco
return _deco
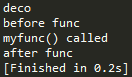
@deco('deco')
def myfunc():
print 'myfunc() called'
myfunc()
测试6
函数参数传递
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(arg):
def _deco(func):
print arg
def __deco(str):
print 'before func'
func(str)
print 'after func'
return __deco
return _deco
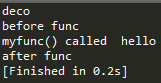
@deco('deco')
def myfunc(str):
print 'myfunc() called ', str
myfunc('hello')
测试7
未知参数个数
复制代码 代码如下:
def deco(arg):
def _deco(func):
print arg
def __deco(*args, **kwargs):
print 'before func'
func(*args, **kwargs)
print 'after func'
return __deco
return _deco
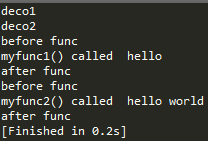
@deco('deco1')
def myfunc1(str):
print 'myfunc1() called ', str
@deco('deco2')
def myfunc2(str1,str2):
print 'myfunc2() called ', str1, str2
myfunc1('hello')
myfunc2('hello', 'world')
测试8
class作为修饰器
复制代码 代码如下:
class myDecorator(object):
def __init__(self, fn):
print "inside myDecorator.__init__()"
self.fn = fn
def __call__(self):
self.fn()
print "inside myDecorator.__call__()"
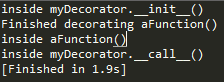
@myDecorator
def aFunction():
print "inside aFunction()"
print "Finished decorating aFunction()"
aFunction()
测试9
复制代码 代码如下:
class myDecorator(object):
def __init__(self, str):
print "inside myDecorator.__init__()"
self.str = str
print self.str
def __call__(self, fn):
def wrapped(*args, **kwargs):
fn()
print "inside myDecorator.__call__()"
return wrapped
@myDecorator('this is str')
def aFunction():
print "inside aFunction()"
print "Finished decorating aFunction()"
aFunction()
实例
给函数做缓存 --- 斐波拉契数列
复制代码 代码如下:
from functools import wraps
def memo(fn):
cache = {}
miss = object()
@wraps(fn)
def wrapper(*args):
result = cache.get(args, miss)
if result is miss:
result = fn(*args)
cache[args] = result
return result
return wrapper
@memo
def fib(n):
if n < 2:
return n
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2)
print fib(10)
注册回调函数 --- web请求回调
复制代码 代码如下:
class MyApp():
def __init__(self):
self.func_map = {}
def register(self, name):
def func_wrapper(func):
self.func_map[name] = func
return func
return func_wrapper
def call_method(self, name=None):
func = self.func_map.get(name, None)
if func is None:
raise Exception("No function registered against - " + str(name))
return func()
app = MyApp()
@app.register('/')
def main_page_func():
return "This is the main page."
@app.register('/next_page')
def next_page_func():
return "This is the next page."
print app.call_method('/')
print app.call_method('/next_page')
mysql封装 -- 很好用
复制代码 代码如下:
import umysql
from functools import wraps
class Configuraion:
def __init__(self, env):
if env == "Prod":
self.host = "coolshell.cn"
self.port = 3306
self.db = "coolshell"
self.user = "coolshell"
self.passwd = "fuckgfw"
elif env == "Test":
self.host = 'localhost'
self.port = 3300
self.user = 'coolshell'
self.db = 'coolshell'
self.passwd = 'fuckgfw'
def mysql(sql):
_conf = Configuraion(env="Prod")
def on_sql_error(err):
print err
sys.exit(-1)
def handle_sql_result(rs):
if rs.rows > 0:
fieldnames = [f[0] for f in rs.fields]
return [dict(zip(fieldnames, r)) for r in rs.rows]
else:
return []
def decorator(fn):
@wraps(fn)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
mysqlconn = umysql.Connection()
mysqlconn.settimeout(5)
mysqlconn.connect(_conf.host, _conf.port, _conf.user,
_conf.passwd, _conf.db, True, 'utf8')
try:
rs = mysqlconn.query(sql, {})
except umysql.Error as e:
on_sql_error(e)
data = handle_sql_result(rs)
kwargs["data"] = data
result = fn(*args, **kwargs)
mysqlconn.close()
return result
return wrapper
return decorator
@mysql(sql = "select * from coolshell" )
def get_coolshell(data):
... ...
... ..
线程异步
复制代码 代码如下:
from threading import Thread
from functools import wraps
def async(func):
@wraps(func)
def async_func(*args, **kwargs):
func_hl = Thread(target = func, args = args, kwargs = kwargs)
func_hl.start()
return func_hl
return async_func
if __name__ == '__main__':
from time import sleep
@async
def print_somedata():
print 'starting print_somedata'
sleep(2)
print 'print_somedata: 2 sec passed'
sleep(2)
print 'print_somedata: 2 sec passed'
sleep(2)
print 'finished print_somedata'
def main():
print_somedata()
print 'back in main'
print_somedata()
print 'back in main'
main()


