表格是唯一的数据结构中Lua可以帮助我们创造出不同的类型,如数组和字典。 Lua使用关联数组和可不仅数字,但也有不同的零字符串索引。表格都没有固定的大小,并根据需要可以增长。
Lua采用的所有陈述,包括包装的代表性表。当我们访问一个方法的字符串。格式,这意味着,我们正在访问的格式化功能的字符串封装。
表示和用法
表称为对象和它们既不值,也没有变。 Lua使用构造函数表达式{}创建一个空表。它是要知道,有保存表的参考和表本身的变量之间没有固定的关系。
复制代码 代码如下:--sample table initialization
mytable = {}
--simple table value assignment
mytable[1]= "Lua"
--removing reference
mytable = nil
-- lua garbage collection will take care of releasing memory
当我们有一个表与集合的元素,如果我们将其指定为b,a和b都指向相同的内存。没有单独的内存单独分配对b。当设置为无,表将仍然可以访问到b。当没有引用表,然后在Lua垃圾收集需要清理过程,使这些未引用的内存再次被重用。
一个例子如下所示用于说明表的上述特征。
复制代码 代码如下:-- Simple empty table
mytable = {}
print("Type of mytable is ",type(mytable))
mytable[1]= "Lua"
mytable["wow"] = "Tutorial"
print("mytable Element at index 1 is ", mytable[1])
print("mytable Element at index wow is ", mytable["wow"])
-- alternatetable and mytable refers to same table
alternatetable = mytable
print("alternatetable Element at index 1 is ", alternatetable[1])
print("mytable Element at index wow is ", alternatetable["wow"])
alternatetable["wow"] = "I changed it"
print("mytable Element at index wow is ", mytable["wow"])
-- only variable released and and not table
alternatetable = nil
print("alternatetable is ", alternatetable)
-- mytable is still accessible
print("mytable Element at index wow is ", mytable["wow"])
mytable = nil
print("mytable is ", mytable)
当我们运行上面的程序,会得到下面的输出
复制代码 代码如下:Type of mytable is table
mytable Element at index 1 is Lua
mytable Element at index wow is Tutorial
alternatetable Element at index 1 is Lua
mytable Element at index wow is Tutorial
mytable Element at index wow is I changed it
alternatetable is nil
mytable Element at index wow is I changed it
mytable is nil
表操作
在对表操作内置函数和它们被列于下表中。
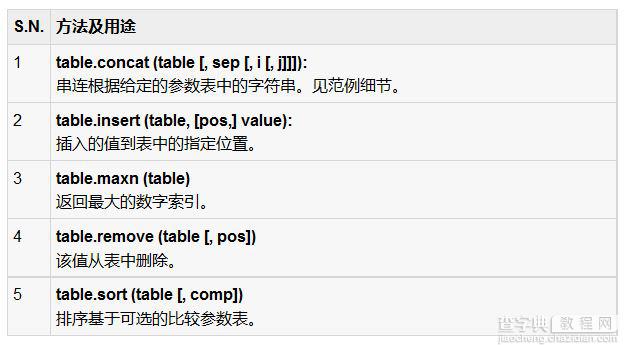
让我们看看上面的函数一些例子。
表串联
我们可以使用concat函数来连接,如下所示的两个表。
复制代码 代码如下:fruits = {"banana","orange","apple"}
-- returns concatenated string of table
print("Concatenated string ",table.concat(fruits))
--concatenate with a character
print("Concatenated string ",table.concat(fruits,", "))
--concatenate fruits based on index
print("Concatenated string ",table.concat(fruits,", ", 2,3))
当我们运行上面的程序,会得到下面的输出
复制代码 代码如下:Concatenated string bananaorangeapple
Concatenated string banana, orange, apple
Concatenated string orange, apple
插入和删除
插入在表中的项目,并除去最常见于表操纵。它下面的解释。
复制代码 代码如下:fruits = {"banana","orange","apple"}
-- insert a fruit at the end
table.insert(fruits,"mango")
print("Fruit at index 4 is ",fruits[4])
--insert fruit at index 2
table.insert(fruits,2,"grapes")
print("Fruit at index 2 is ",fruits[2])
print("The maximum elements in table is",table.maxn(fruits))
print("The last element is",fruits[5])
table.remove(fruits)
print("The previous last element is",fruits[5])
当我们运行上面的程序,会得到下面的输出
复制代码 代码如下:Fruit at index 4 is mango
Fruit at index 2 is grapes
The maximum elements in table is5
The last element ismango
The previous last element isnil
排序表格
排序表通常需要和排序函数表中的元素按字母顺序排序。下图所示为这方面的一个范例。
复制代码 代码如下:fruits = {"banana","orange","apple","grapes"}
for k,v in ipairs(fruits) do
print(k,v)
end
table.sort(fruits)
print("sorted table")
for k,v in ipairs(fruits) do
print(k,v)
end
当我们运行上面的程序,会得到下面的输出
复制代码 代码如下:1banana
2orange
3apple
4grapes
sorted table
1apple
2banana
3grapes
4orange


