本文实例讲述了Android基于Sensor感应器获取重力感应加速度的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
FETC项目指导老师提出了新的需求,想要在游戏地图中表现出用户用户当期移动的方向,再用GPS的话显然很不靠谱,所以想到了android强大的感应器。。。
很多移动设备都内置了感应器,android通过Sensor和SensorManager类抽象了这些感应器,通过这些类可以使用android设备的传感器
一 介绍Sensor类
SDK只有一句介绍“Class representing a sensor. Use getSensorList(int) to get the list of available Sensors.”,表示一个感应器的类,可以使用getSensorList方法(此方法属于接下来要讲的SensorManager)获得所有可用的感应器,该方法返回的是一个List<Sensor>
下面的列表显示了,Sensor所提供的所有服务
Constants
int TYPE_ACCELEROMETER A constant describing an accelerometer sensor type.
//三轴加速度感应器 返回三个坐标轴的加速度 单位m/s2
int TYPE_ALL A constant describing all sensor types.
//用于列出所有感应器
int TYPE_GRAVITY A constant describing a gravity sensor type.
//重力感应器
int TYPE_GYROSCOPE A constant describing a gyroscope sensor type
//陀螺仪 可判断方向 返回三个坐标轴上的角度
int TYPE_LIGHT A constant describing an light sensor type.
//光线感应器 单位 lux 勒克斯
int TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION A constant describing a linear acceleration sensor type.
//线性加速度
int TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD A constant describing a magnetic field sensor type.
//磁场感应 返回三个坐标轴的数值 微特斯拉
int TYPE_ORIENTATION This constant is deprecated. use SensorManager.getOrientation() instead.
//方向感应器 已过时 可以使用方法获得
int TYPE_PRESSURE A constant describing a pressure sensor type
//压力感应器 单位 千帕斯卡
int TYPE_PROXIMITY A constant describing an proximity sensor type.
//距离传感器
int TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR A constant describing a rotation vector sensor type.
//翻转传感器
int TYPE_TEMPERATURE A constant describing a temperature sensor type
//温度传感器 单位 摄氏度
此类中包含的方法都是get型的 用来获取所选sensor的一些属性,sensor类一般不需要new而是通过SensorManager的方法获得
二 介绍SensorManager类
SDK解释:“SensorManager lets you access the device's sensors. Get an instance of this class by calling Context.getSystemService() with the argument SENSOR_SERVICE.
Always make sure to disable sensors you don't need, especially when your activity is paused. Failing to do so can drain the battery in just a few hours. Note that the system will not disable sensors automatically when the screen turns off. ”
SensorManager 允许你访问设备的感应器。通过传入参数SENSOR_SERVICE参数调用Context.getSystemService方法可以获得一个sensor的实例。永远记得确保当你不需要的时候,特别是Activity暂定的时候,要关闭感应器。忽略这一点肯能导致几个小时就耗尽电池,注意当屏幕关闭时,系统不会自动关闭感应器。
三 常用的感应器
(1) 加速度感应器
可以通过这个感应器获得三个浮点型
x-axis
y-axis
z-axis
可参阅《android 高级编程2》中的一个插图分析次数据
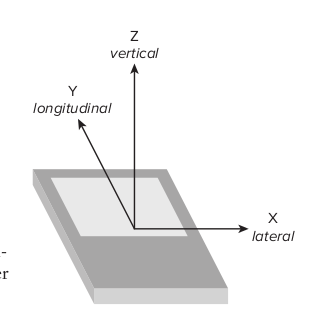
X Y Z分别对应values[0]到[2]
X表示左右移动的加速度
Y表示前后移动的加速度
Z表示垂直方向的加速度 (测试时发现,将手机置于水平桌面稳定后 XY均为0 Z的值为9.4 约等于重力加速度,依次可以做一个简单的算法实现重力测力计,有时间会给大家一个例子)
下面先看一个基本的获取加速的demo,希望大家好好注意代码中的注释
/* * @author octobershiner * 2011 07 27 * SE.HIT * 一个演示android加速度感应器的例子 * */ package uni.sensor; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Context; import android.hardware.Sensor; import android.hardware.SensorEvent; import android.hardware.SensorEventListener; import android.hardware.SensorManager; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; public class SensorDemoActivity extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ //设置LOG标签 private static final String TAG = "sensor"; private SensorManager sm; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); //创建一个SensorManager来获取系统的传感器服务 sm = (SensorManager)getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE); //选取加速度感应器 int sensorType = Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER; /* * 最常用的一个方法 注册事件 * 参数1 :SensorEventListener监听器 * 参数2 :Sensor 一个服务可能有多个Sensor实现,此处调用getDefaultSensor获取默认的Sensor * 参数3 :模式 可选数据变化的刷新频率 * */ sm.registerListener(myAccelerometerListener,sm.getDefaultSensor(sensorType),SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL); } /* * SensorEventListener接口的实现,需要实现两个方法 * 方法1 onSensorChanged 当数据变化的时候被触发调用 * 方法2 onAccuracyChanged 当获得数据的精度发生变化的时候被调用,比如突然无法获得数据时 * */ final SensorEventListener myAccelerometerListener = new SensorEventListener(){ //复写onSensorChanged方法 public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent sensorEvent){ if(sensorEvent.sensor.getType() == Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER){ Log.i(TAG,"onSensorChanged"); //图解中已经解释三个值的含义 float X_lateral = sensorEvent.values[0]; float Y_longitudinal = sensorEvent.values[1]; float Z_vertical = sensorEvent.values[2]; Log.i(TAG,"n heading "+X_lateral); Log.i(TAG,"n pitch "+Y_longitudinal); Log.i(TAG,"n roll "+Z_vertical); } } //复写onAccuracyChanged方法 public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor , int accuracy){ Log.i(TAG, "onAccuracyChanged"); } }; public void onPause(){ /* * 很关键的部分:注意,说明文档中提到,即使activity不可见的时候,感应器依然会继续的工作,测试的时候可以发现,没有正常的刷新频率 * 也会非常高,所以一定要在onPause方法中关闭触发器,否则讲耗费用户大量电量,很不负责。 * */ sm.unregisterListener(myAccelerometerListener); super.onPause(); } }
测试的时候会发现刷新的特别快,这就引出一个问题,如果真的要呈现在UI中的话,就会不断的绘制界面,非常耗费资源,所以《android高级编程》中给出了一个方案就是引入新的线程来刷新界面,明天有时间的话,尽量把把例子给大家。
希望本文所述对大家Android程序设计有所帮助。


