由于一个项目的需要,我研究了一下android的网络通信方式,大体和java平台的很相似!
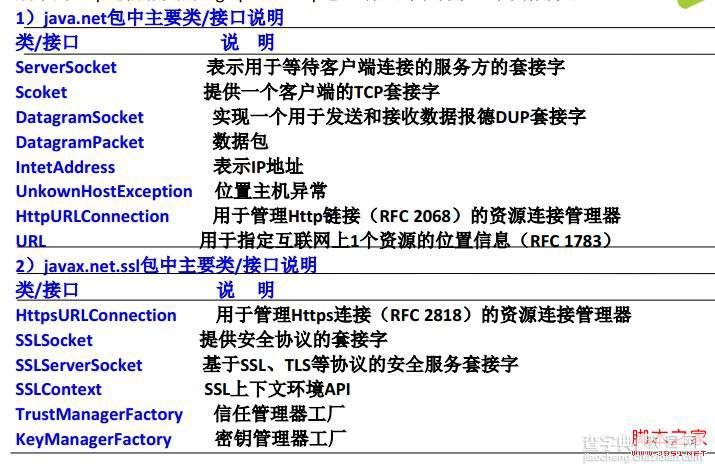
android平台也提供了很多的API供开发者使用,请按示例图:

首先,介绍一下通过http包工具进行通信,分get和post两种方式,两者的区别是:
1,post请求发送数据到服务器端,而且数据放在html header中一起发送到服务器url,数据对用户不可见,get请求是把参数值加到url的队列中,这在一定程度上,体现出post的安全性要比get高
2,get传送的数据量小,一般不能大于2kb,post传送的数据量大,一般默认为不受限制。
访问网络要加入权限 <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
下面是get请求HttpGet时的示例代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
View Code
// 创建DefaultHttpClient对象
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
// 创建一个HttpGet对象
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(
"http://192.168.1.88:8888/foo/secret.jsp");
try
{
// 发送GET请求
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(get);
HttpEntity entity = httpResponse.getEntity();
if (entity != null)
{
// 读取服务器响应
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(entity.getContent()));
String line = null;
response.setText("");
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null)
{
// 使用response文本框显示服务器响应
response.append(line + "n");
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
post请求HttpPost的示例代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
View Code
HttpClient httpClient=new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(
"http://192.168.1.88:8888/foo/login.jsp");
// 如果传递参数个数比较多的话可以对传递的参数进行封装
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("name", name));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("pass", pass));
try
{
// 设置请求参数
post.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(
params, HTTP.UTF_8));
// 发送POST请求
HttpResponse response = httpClient
.execute(post);
// 如果服务器成功地返回响应
if (response.getStatusLine()
.getStatusCode() == 200)
{
String msg = EntityUtils
.toString(response.getEntity());
// 提示登录成功
Toast.makeText(HttpClientTest.this,
msg, 5000).show();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
其次,介绍一下,使用java包的工具进行通信,也分get和post方式
默认使用get方式,示例代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
View Code
try
{
String urlName = url + "?" + params;
URL realUrl = new URL(urlName);
// 打开和URL之间的连接或者HttpUrlConnection
URLConnection conn =realUrl.openConnection();
// 设置通用的请求属性
conn.setRequestProperty("accept", "*/*");
conn.setRequestProperty("connection", "Keep-Alive");
conn.setRequestProperty("user-agent",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1)");
// 建立实际的连接
conn.connect();
// 获取所有响应头字段
Map<String, List<String>> map = conn.getHeaderFields();
// 遍历所有的响应头字段
for (String key : map.keySet())
{
System.out.println(key + "--->" + map.get(key));
}
// 定义BufferedReader输入流来读取URL的响应
in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null)
{
result += "n" + line;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("发送GET请求出现异常!" + e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 使用finally块来关闭输入流
使用post的示例代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
View Code
try
{
URL realUrl = new URL(url);
// 打开和URL之间的连接
URLConnection conn = realUrl.openConnection();
// 设置通用的请求属性
conn.setRequestProperty("accept", "*/*");
conn.setRequestProperty("connection", "Keep-Alive");
conn.setRequestProperty("user-agent",
"Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1)");
// 发送POST请求必须设置如下两行
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setDoInput(true);
// 获取URLConnection对象对应的输出流
out = new PrintWriter(conn.getOutputStream());
// 发送请求参数
out.print(params);
// flush输出流的缓冲
out.flush();
// 定义BufferedReader输入流来读取URL的响应
in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null)
{
result += "n" + line;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("发送POST请求出现异常!" + e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
从以上知,get请求只需要conn.connect(),post请求时,必须设置 conn.setDoOutput(true),conn.setDoinput(true),还必须获取URLConnection的输出流getOutputStream()
最后,使用套接字(soket)进行通信分为两种形式:面向连接的(tcp)和无连接的(udp 数据报)
tcp连接示例:
复制代码 代码如下:
View Code
//服务器端
//创建一个ServerSocket,用于监听客户端Socket的连接请求
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(30000);
//采用循环不断接受来自客户端的请求
while (true)
{
//每当接受到客户端Socket的请求,服务器端也对应产生一个Socket
Socket s = ss.accept();
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("您好,您收到了服务器的消息!n"
.getBytes("utf-8"));
//关闭输出流,关闭Socket
os.close();
s.close();
}
//客户端
Socket socket = new Socket("192.168.1.88" , 30000);
//将Socket对应的输入流包装成BufferedReader
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
//进行普通IO操作
String line = br.readLine();
show.setText("来自服务器的数据:" + line);
br.close();
socket.close();
udp连接示例:
复制代码 代码如下:
View Code
服务器端:
try {
//创建一个DatagramSocket对象,并指定监听的端口号
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(4567);
byte data [] = new byte[1024];
//创建一个空的DatagramPacket对象
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,data.length);
//使用receive方法接收客户端所发送的数据
socket.receive(packet);
String result = new String(packet.getData(),packet.getOffset(),packet.getLength());
System.out.println("result--->" + result);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
客户端:
try {
//首先创建一个DatagramSocket对象
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(4567);
//创建一个InetAddree
InetAddress serverAddress = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.1.104");
String str = "hello";
byte data [] = str.getBytes();
//创建一个DatagramPacket对象,并指定要讲这个数据包发送到网络当中的哪个地址,以及端口号
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,data.length,serverAddress,4567);
//调用socket对象的send方法,发送数据
socket.send(packet);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
以上,是我的总结,最近正在做一个类似网络视频客户端的作品,如果大家有人做过这方面,欢迎您们提出建议和实现终端和服务器访问的其他方法。谢谢!
与大家共勉!!!


